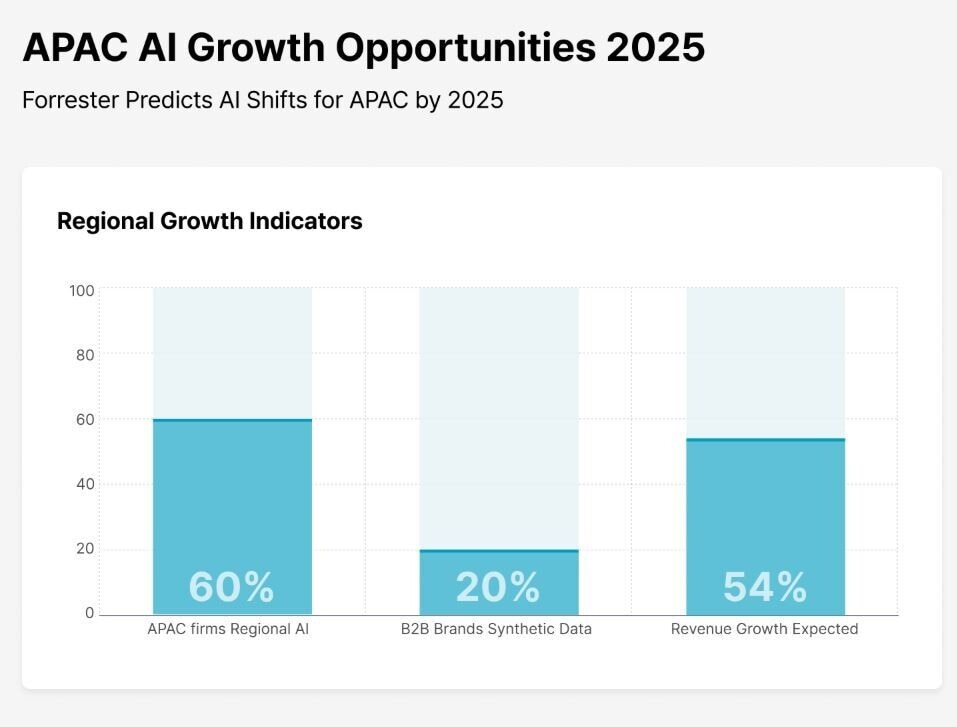
[2025] AI Adoption's Impact on Asia-Pacific Jobs
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The AI Surge and Its Global Ripple
- AI's Booming Presence in Wealthy Nations
- The Economic Divide: Winners and Losers
- AI and Job Displacement: Who's at Risk?
- AI's Double-Edged Sword for Developing Countries
- AI's Economic Potential: Trillions at Stake
- Case Studies: China, Singapore, and South Korea
- Challenges for South Asian Nations
- Job Protection Strategies: Balancing Ethics and Progress
- The Role of Basic Digital Access
- AI Innovation Hubs: A Regional Overview
- AI's Impact on GDP and Productivity
- Unequal Playing Fields: A Regional Analysis
- AI Misuse and Human Rights Concerns
- Empowering Women and Youth in the Age of AI
- FAQs: AI and Job Markets
- Conclusion: Navigating the AI Frontier
Introduction: The AI Surge and Its Global Ripple
In recent years, the rapid adoption of artificial intelligence (AI) has become a defining feature of our technological landscape. From revolutionizing industries to reshaping economies, AI’s impact is undeniable. But let's be real for a second—while the AI wave is creating new opportunities, it's also putting millions of jobs at risk, especially in the Asia-Pacific region. This isn't just tech evolution; it's a seismic shift with global implications.
The United Nations has sounded the alarm, warning that the AI boom could mirror the industrial revolutions of the past, splitting the world into tech haves and have-nots [1]. Just imagine the 19th-century industrialization on steroids, where countries with the foresight to invest in AI reap massive benefits, leaving others trailing far behind. In this article, we dive deep into this unfolding story, examining the winners, the losers, and the future of work in the Asia-Pacific.
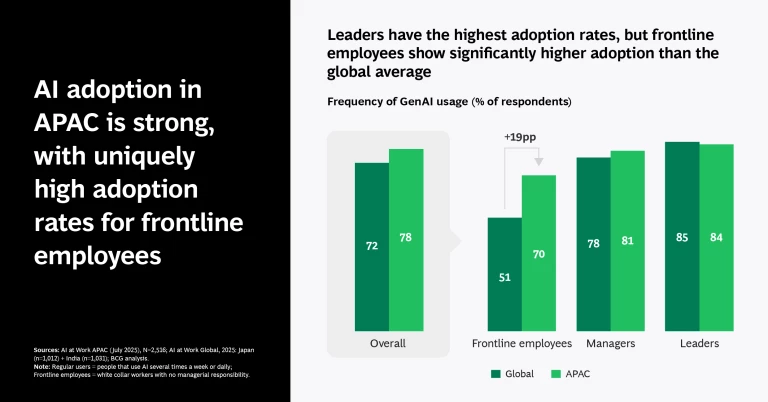
AI's Booming Presence in Wealthy Nations
Let's start with the obvious: AI is thriving in wealthy nations. Countries like the United States, Japan, and Germany have poured billions into AI research and development, creating a technological edge that’s hard to beat [2]. These countries aren’t just investing in AI—they're embedding it into the very fabric of their economies. According to recent studies, these nations account for over 70% of global AI research output and innovation [3].
But why does this matter? Well, the economic benefits are staggering. AI is projected to contribute over $15 trillion to the global economy by 2030 [4]. That’s not just a number; it’s a testament to the transformative potential of AI, primarily concentrated in countries that can afford to lead the charge. For these nations, AI is not just a tool; it's a strategic asset.
Key Drivers of AI Growth
- Investment in R&D: Wealthy nations are leading the way in AI research, with robust funding channels and cutting-edge facilities [5].
- High Digital Literacy: A tech-savvy workforce ready to adapt and innovate with AI technologies [6].
- Supportive Policies: Governments are crafting AI-friendly regulations and guidelines that spur growth [7].
The Economic Divide: Winners and Losers
AI's rise is creating a new economic divide. On one side, we have countries that are embracing AI with open arms, and on the other, nations that lack the resources to keep up. The disparity is not just about technology—it's about economic survival [8].
Winners
- Tech-Driven Economies: Countries leading in AI development are seeing a surge in productivity and economic growth [9].
- Innovative Industries: Sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing are experiencing unprecedented efficiency and innovation gains [10].
Losers
- Developing Nations: These countries face the dual challenge of limited AI investment and a workforce vulnerable to automation [11].
- Entry-Level Workers: Jobs that require minimal skills are at the highest risk of being replaced by AI-driven automation [12].
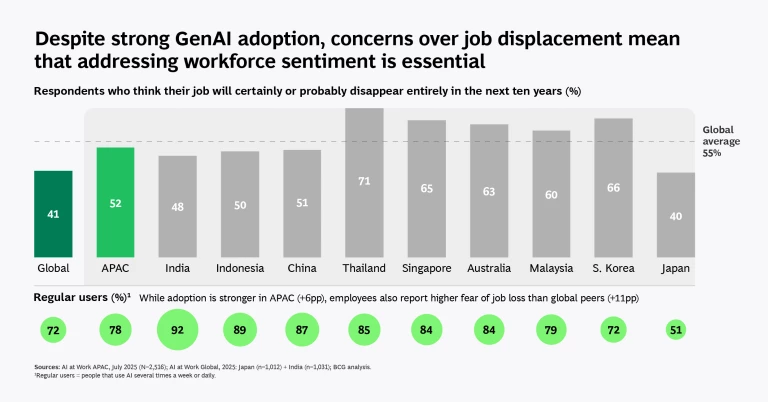
AI and Job Displacement: Who's at Risk?
Now, let's talk about the elephant in the room—job displacement. AI is changing the employment landscape, and not everyone is prepared for it. Estimates suggest that up to 30% of jobs in certain sectors could be automated by 2030 [2]. For the Asia-Pacific, this means millions of jobs, particularly in manufacturing and service industries, are in jeopardy [14].
High-Risk Sectors
- Manufacturing: Automation is rapidly replacing manual labor, leading to factory job losses [15].
- Retail and Services: AI-driven customer service platforms are reducing the need for human interaction [16].
Vulnerable Demographics
- Women and Youth: These groups often occupy roles that are more susceptible to automation [17].
- Low-Skilled Workers: Without access to reskilling opportunities, these workers face significant barriers to employment [18].
AI's Double-Edged Sword for Developing Countries
For developing countries, AI is both an opportunity and a threat. On one hand, it offers the potential for economic growth and improved efficiency. On the other, it poses significant risks, particularly for countries lacking the infrastructure to support AI integration [19].
Opportunities
- Economic Growth: AI can drive productivity and innovation, leading to economic gains [20].
- Improved Services: AI can enhance public services like healthcare and education, offering better outcomes for citizens [21].
Threats
- Job Losses: Without the capacity to integrate AI effectively, job displacement could lead to increased unemployment [22].
- Digital Divide: The gap between those with access to AI and those without could widen, exacerbating existing inequalities [23].
AI's Economic Potential: Trillions at Stake
Let’s not forget the financial aspect. AI's economic potential is enormous. In the Asia-Pacific region alone, AI is expected to inject nearly $1 trillion in economic gains over the next decade [24]. This isn’t just about profit margins; it’s about transforming entire economies.
Economic Impact
- GDP Growth: AI is projected to boost GDP by around two percentage points annually [25].
- Productivity Gains: Sectors such as health and finance could see productivity increases of up to 5% [26].

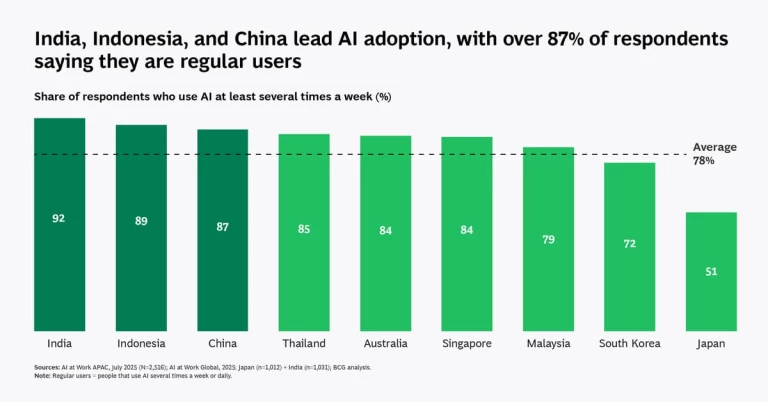
Case Studies: China, Singapore, and South Korea
Some countries are setting the pace in AI adoption, and their stories offer valuable insights.
China: The AI Powerhouse
China is leading the charge, with 70% of global AI patents and a thriving tech ecosystem [27]. The government’s strategic focus on AI is driving innovation and economic growth [28].
Singapore: A Smart Nation
Singapore's Smart Nation initiative is a testament to its commitment to AI. This city-state is leveraging AI to enhance public services and improve the quality of life for its citizens [29].
South Korea: Tech-Driven Growth
South Korea is investing heavily in AI, with government policies that encourage innovation and support tech startups [30].
Challenges for South Asian Nations
For many South Asian countries, the AI revolution brings unique challenges. Limited infrastructure, skills, and investment in AI are significant barriers to entry [31].
Infrastructure Gaps
- Digital Access: Many regions lack the basic digital infrastructure needed for AI integration [32].
- Governance: Weak governance systems can hinder effective AI deployment [33].
Skill Shortages
- Education and Training: There is a critical need for education and training programs to upskill the workforce [34].
Job Protection Strategies: Balancing Ethics and Progress
Protecting jobs in the age of AI is a complex challenge. Governments and companies must balance the ethical implications of AI with the need for economic progress [35].
Ethical AI Implementation
- Inclusive Policies: Ensure AI deployment is inclusive, considering the needs of vulnerable populations [36].
- Regulatory Frameworks: Develop frameworks that guide ethical AI use and protect workers’ rights [37].
Reskilling and Upskilling
- Education Programs: Invest in education programs that equip workers with the skills needed for AI-related jobs [38].
The Role of Basic Digital Access
Access to digital technology is a fundamental requirement for harnessing AI's benefits. In regions where digital access is limited, the potential of AI remains untapped [39].
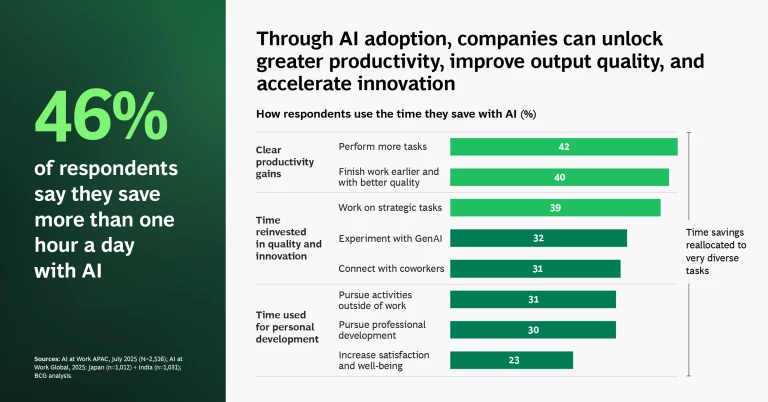
AI Innovation Hubs: A Regional Overview
The Asia-Pacific region is home to several AI innovation hubs, driving research and development [40].
Key Hubs
- China: Leading in AI research and development [41].
- India: Emerging as a major player in AI innovation [42].
- Japan: Combining AI with robotics to create new opportunities [43].
AI's Impact on GDP and Productivity
AI is not just a technological advancement—it’s an economic game-changer. Its impact on GDP and productivity is profound [44].
GDP Boost
- Annual Growth: AI could lift annual GDP growth by up to two percentage points in the region [45].
Productivity
- Sectoral Gains: Sectors like healthcare and finance are experiencing significant productivity gains [46].

Unequal Playing Fields: A Regional Analysis
The Asia-Pacific region is marked by stark inequalities in AI adoption and benefits. While some countries are reaping the rewards, others are struggling to keep up [47].
Inequality Drivers
- Economic Disparities: Wealthier nations are better positioned to invest in AI [48].
- Infrastructure: Countries with advanced infrastructure have a significant advantage [49].
AI Misuse and Human Rights Concerns
AI’s misuse poses serious human rights challenges. From privacy violations to biased algorithms, the risks are real [50].
Key Concerns
- Data Privacy: Ensuring AI systems respect user privacy and data security [51].
- Bias and Discrimination: Addressing biases in AI algorithms to prevent discrimination [21].
Empowering Women and Youth in the Age of AI
Women and youth are often the most affected by AI-driven job displacement. Empowering these groups is crucial for ensuring inclusive economic growth [53].
Empowerment Strategies
- Education and Training: Provide targeted education and training programs [54].
- Policy Support: Develop policies that support women and youth in the workforce [55].
FAQs: AI and Job Markets
-
How is AI affecting job markets in the Asia-Pacific?
- AI is transforming job markets by automating tasks and creating new opportunities in tech-driven sectors [2].
-
What sectors are most impacted by AI?
- Manufacturing, retail, and services are among the most impacted sectors, facing significant automation [57].
-
Can AI create more jobs than it displaces?
- While AI creates new job opportunities, the net impact depends on the pace of reskilling and adaptation [58].
-
How can developing countries benefit from AI?
- By investing in digital infrastructure and education, developing countries can harness AI for economic growth [59].
-
What are the ethical concerns surrounding AI?
- Key concerns include privacy violations, algorithmic bias, and the need for ethical governance frameworks [60].
Conclusion: Navigating the AI Frontier
As we navigate the complexities of the AI frontier, it's clear that the stakes are high. The Asia-Pacific region stands at a crossroads, with the potential to harness AI for unprecedented economic growth or face the challenges of increased inequality and job displacement. The path forward requires strategic investments, ethical considerations, and a commitment to inclusive growth. Let's embrace the opportunities AI presents while ensuring that its benefits are shared equitably across the region [61].
Key Takeaways:
- AI's economic impact is massive, with trillions at stake.
- Developing nations face unique challenges in AI adoption.
- Job displacement is a significant risk, particularly for low-skilled workers.
- Ethical AI implementation and reskilling are crucial for mitigating risks.
- Empowering women and youth is essential for inclusive growth.
Key Takeaways
- AI's economic impact is massive, with trillions at stake.
- Developing nations face unique challenges in AI adoption.
- Job displacement is a significant risk, particularly for low-skilled workers.
- Ethical AI implementation and reskilling are crucial for mitigating risks.
- Empowering women and youth is essential for inclusive growth.
![[2025] AI Adoption's Impact on Asia-Pacific Jobs](https://blog.theinterviewguys.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/ai-adoption-explosion.jpg)